Respiratory system is also involved in thermoregulation the regulated of body temperature.
Day 1 → learn Day 2 → quick review Day 4 → test yourself Day 7 → review again Draw mind maps, flow charts, or color-coded notes. For example, when studying the endocrine system, draw glands with arrows showing hormone flow. The brain remembers images better than plain text. Teach Someone Else Teaching or explaining a topic out loud forces you to organize your thoughts clearly. If you can explain it simply, you really understand it.
Thursday, September 11, 2025
conductive zone
conductive zone brings inhaled air to the respiratory where gas exchange occurs.
diaphragm and intercostal muscles involved in breathing.
external respiration exchange of gas between the lungs and the blood
Internal respiration exchange of gas between blood and tissue.
Secondary function of respiratory system includes blood PH regulation of the blood, thermoregulation odor detection and the production of speech.
coronal plane or frontal plane
Divide the body or any body structure vertically into front and back anterior and posterior sections.
The coronal plane runs vertically through the body at right angles to the midline.
Dorsal cavity
Which of the following is not found in the dorsal cavity of the body?
- cerebellum
- heart
- brainstem
- spine
Distal
Which term distal refer to
(1) Position towards the front of the body
(2) Position towards the back of the body
(3) Position away from the where the limb is attached to the body.
(4) Position near where the limb is attached to the body.
example Distal radius refers to a location in the forearm close to the wrist.
proximal refer the position near where the limb is attached to the body.
Anterior refers to the front whereas posterior refers to the back.
Superior is a term that refers to a position near the head whereas inferi
transverse plane
transverse plane also called axial
Cross sectional or horizontal plane
Divides the body into horizontal plane divides the body into superior and inferior portions
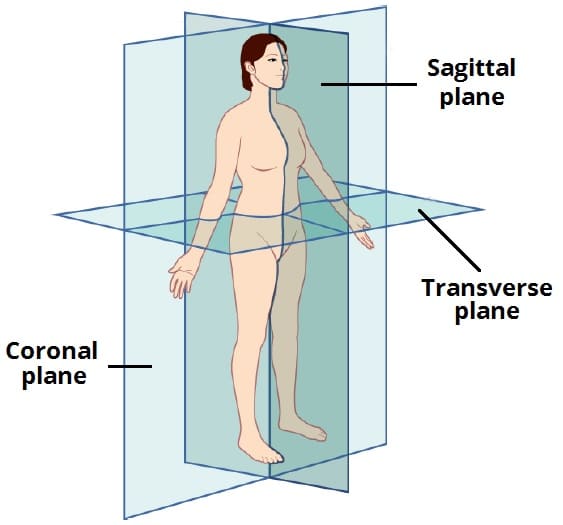
Sagittal Plane
The sagittal plane is a vertical plane which passes through the body longitudinally. It divides the body into a left section and a right section.
A specific sagittal plane is the median sagittal plane – which passes down the midline of the body, separating it into equal halves.
Coronal Plane
The coronal plane is a vertical plane which also passes through the body longitudinally – but perpendicular (at a right angle) to the sagittal plane.
It divides the body into a front (anterior) section and back (posterior) section.
Transverse Plane
The transverse plane is a horizontal plane. It is perpendicular to both the sagittal and coronal planes, and parallel to the ground.
It divides the body into an upper (superior) section and a lower (inferior) section.
Transverse planes are also known as transaxial planes or axial planes.
4 quadrants or 9 regions
From anatomy viewpoint the urinary bladder belongs to which system?
- The hypogastric region
- The right upper region
- The umbilical region
- The left lower quadrant
The left lower quadrant (LLQ) of the human abdomen is the area left of the midline and below the umbilicus. The LLQ includes the left iliac fossa and half of the left flank region. The equivalent term for animals is left posterior quadrant. Important organs here are:
- the descending colon and sigmoid colon
- the left ovary and fallopian tube
- the left ureter
The left upper quadrant (LUQ) extends from the median plane to the left of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage. The equivalent term for animals is left anterior quadrant. Important organs here are:
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Left lobe of liver
- Body of pancreas
- Left kidney and adrenal gland
- Splenic flexure of colon
- Parts of transverse and descending colon
The right upper quadrant (RUQ) extends from the median plane to the right of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent term for animals is right anterior quadrant. Important organs here are:
- Liver
- Gall bladder with biliary tree
- Duodenum
- Head of pancreas
- Right kidney and adrenal gland
- Hepatic flexure of colon
The right lower quadrant (RLQ) extends from the median plane to the right of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the right inguinal ligament. The equivalent term for animals is right posterior quadrant. Important organs here are:
- Cecum
- Appendix
- Ascending colon
- Right ovary and fallopian tube
- Right ureter
Regions


Nine regions of the abdomen can be marked using two horizontal and two vertical dividing lines. The vertical lines are the mid-clavicular lines taken from the mid-point of each clavicle. The upper horizontal line is the subcostal line taken from the inferior parts of the lowest costal cartilages. The lower horizontal line is the transtubercular line connecting the tubercles of the pelvis.[3][4]
The three main centrally positioned regions are the epigastric region, th